
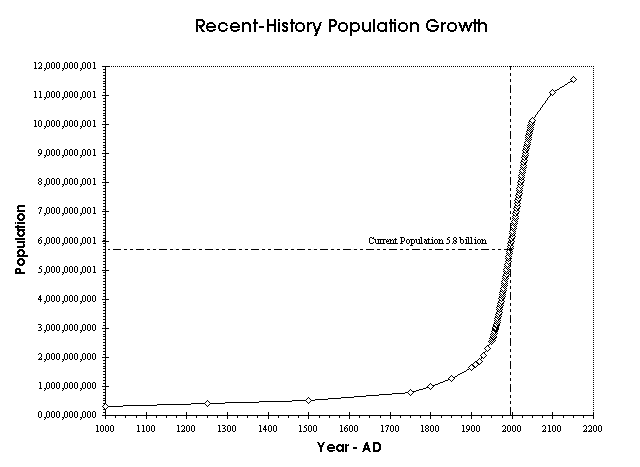
The population of Europe was more than 70 million in 1340. The Plague of Justinian, which first emerged during the reign of the Roman emperor Justinian, caused Europe's population to drop by around 50% between the 6th and 8th centuries AD. By contrast, it is estimated that around 50–60 million people lived in the combined eastern and western Roman Empire in the 4th century AD. Even earlier, genetic evidence suggests humans may have gone through a population bottleneck of between 1,000 and 10,000 people about 70,000 BC, according to the Toba catastrophe theory. Main articles: Classical demography and Medieval demographyĮstimates of the population of the world at the time agriculture emerged in around 10,000 BC have ranged between 1 million and 15 million. Antarctica only has a very small, fluctuating population of about 1200 people based mainly in polar science stations. Northern America, primarily consisting of the United States and Canada, has a population of around 368 million (5%), and Oceania, the least populated region, has about 42 million inhabitants (0.5%). Europe's 747 million people make up 10% of the world's population as of 2020, while the Latin American and Caribbean regions are home to around 653 million (8%). Africa is the second most populated continent, with around 1.34 billion people, or 17% of the world's population. The world's two most populated countries, China and India, together constitute about 36% of the world's population. Asia is the most populous continent, with its 4.64 billion inhabitants accounting for 60% of the world population. Six of the Earth's seven continents are permanently inhabited on a large scale. The median age of human beings as of 2020 is 31 years. The total number of deaths is currently 57 million/year and is projected to grow steadily to 121 million/year by 2100. The total number of births globally is currently (2015-20) 140 million/year, is projected to peak during the period 2040-45 at 141 million/year and thereafter decline slowly to 126 million/year by 2100. Other demographers predict that the human population will begin to decline in the second half of the 21st century. The UN Department of Economics and Social Affairs projects between 9 and 10 billion people by 2050, and gives an 80% confidence interval of 10–12 billion by the end of the 21st century, with a growth rate by then of zero. The global population is still increasing, but there is significant uncertainty about its long-term trajectory due to changing rates of fertility and mortality. The growth rate declined to 1.1% between 20 and is projected to decline further in the course of the 21st century. The highest global population growth rates, with increases of over 1.8% per year, occurred between 19 – peaking at 2.1% between 19. The human population has experienced continuous growth following the Great Famine of 1315–1317 and the end of the Black Death in 1350, when it was near 370,000,000. It took over two million years of human prehistory and history for the human population to reach one billion and only 207 years more to grow to 7 billion. In demographics, the term world population is often used to refer to the total number of humans currently living, and was estimated to have exceeded 7.9 billion as of November 2021. Sources are given at the end of the page.High, medium, and low projections of the future human world population They are presented as illustrative of the development of global demographic trends. They are not of uniform reliability or methodology and may not represent uniform time series. The following historical population figures are compiled from multiple sources. Historical world population data Historical World Population Data


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
